How Hot Can a GPU Get Before Damage? Things You Should Know
Ever felt the warmth emanating from your computer during a heavy gaming session or while running high-intensity tasks? That’s your GPU hard at work. The question is, just how hot can it get before damaged?
While modern GPUs are built to handle the heat, every hardware has its limits. Pushing a GPU beyond these limits consistently can lead to damages, both immediate and over time. Generally, most GPUs can safely run between 60°C-70°C without any issues. However, it’s when temperatures rise above 85°C that problems can start to arise.
Interested in understanding the mechanics, repercussions, and preventive measures for GPU overheating? Stay tuned as we take a thermal journey into the world of GPUs.
How Hot is Too Hot for GPU?
Every GPU, whether from Nvidia, AMD, or any other manufacturer, has a safe temperature range. This range varies somewhat between models and brands, but there are general guidelines:
- Idle Temperatures: When your computer isn’t running any graphics-intensive applications, your GPU should be at its idle temperature. For most modern GPUs, this is typically between 30°C to 50°C.
- Load Temperatures: When running high-end games or graphic-intensive tasks, the GPU’s temperature will rise. Generally, a temperature of 60°C to 80°C under load is considered safe for most GPUs.
The Critical Zone
- Above 80°C: If your GPU temperature consistently surpasses 80°C, it’s entering a potentially risky zone. While many modern GPUs are designed to handle temperatures up to the 90°C-100°C range, consistently operating in this zone can have adverse long-term effects on the GPU’s lifespan and performance.
- Above 90°C: Consistent temperatures above 90°C are a significant cause for concern. At this point, you might notice reduced performance, system instability, or graphical anomalies due to the GPU throttling itself to prevent damage.
- The 100°C Mark: If a GPU reaches or exceeds 100°C, it’s entering a danger zone. Most modern GPUs will shut down or drastically throttle themselves before reaching this point. Prolonged operation at these temperatures can cause immediate and severe damage.
Factors Influencing GPU Temperatures
Several elements can influence how hot a GPU gets:
- Ambient room temperature: A hotter environment naturally leads to increased GPU temps.
- Airflow within the PC case: Poor case ventilation can trap heat.
- GPU workload: More intensive tasks will generate more heat.
- Cooling solutions: Stock coolers versus aftermarket solutions can make a difference.
Now, let’s see what will happen if your GPU gets too hot for too long.
Dangers of Overheating GPUs
A short spike to high temperatures is less concerning than consistently operating at those temperatures. For example, hitting 90°C for a few seconds during an intense gaming session might not be as harmful as maintaining 90°C over hours of operation.
Let’s identify what can high head do to your GPU and when it is a matter of concern:
Immediate, Short-term Effects
- System Instability: One of the first signs of an overheating GPU is system instability. This can manifest as random reboots, screen freezes, or the dreaded blue screen of death (BSOD).
- Screen Artifacts: Overheating can cause graphical anomalies, known as artifacts. These can appear as random lines, dots, or colors that shouldn’t be there. They’re often a precursor to more severe problems.
- Throttling: Modern GPUs are designed to reduce their clock speed when they reach a certain temperature to prevent damage. This throttling can significantly reduce your GPU’s performance, leading to lag in games and slower rendering times in graphical software.
- Shutdowns: If the GPU temperature continues to rise and reaches a critical limit, the computer might shut down entirely to prevent any hardware damage.
Long-term Repercussions
- Reduced GPU Lifespan: Consistent exposure to high temperatures can weaken the GPU’s components, leading to a reduced lifespan. What might have served you well for 5-6 years could now give up within 2-3 years.
- Permanent Damage to Components: Over time, excessive heat can damage the GPU’s silicon and other components. This damage can cause permanent artifacts, reduced performance, or complete GPU failure.
- Impact on Nearby Components: The GPU isn’t the only component in your PC. Consistent overheating can raise the internal temperature of your PC case, affecting other components like RAM, the motherboard, and even the CPU.
- Potential Data Loss: Unexpected shutdowns or reboots can lead to data corruption, especially if data was being written or read at the time of the shutdown. This can result in loss of unsaved work or, in extreme cases, corruption of entire partitions.
- Decreased Overall System Performance: An overheating GPU can lead to system-wide slowdowns, affecting not just games or graphic-intensive tasks but everyday tasks like web browsing or word processing.
Tips to Prevent GPU Overheating
- Monitor GPU Temperatures
- Ensure good airflow in your PC case.
- Clean the GPU and its cooler regularly to remove dust.
- Consider aftermarket cooling solutions.
- Manage the room temperature.
- Ensure the GPU fan is functioning.
Wrapping Up
In the blazing-fast world of graphics processing, heat is a byproduct we can’t ignore. While GPUs are sturdy pieces of technology, they’re not invincible. By being vigilant, monitoring temperatures, and ensuring our GPUs remain cool, we can enjoy smooth graphics for years to come. Remember, it’s not just about performance, but longevity and safety. Take good care of your GPU, and it’ll take care of your gaming needs. Thanks for reading, and may your frames be high and temperatures low!
Frequently Asked Questions:
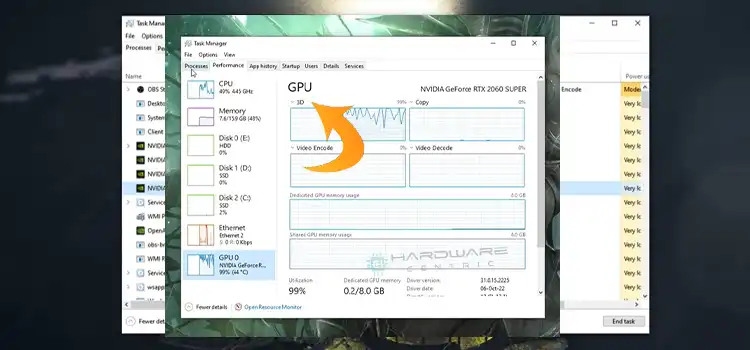
- How can I check my GPU’s temperature?
- Use software utilities like GPU-Z, HWMonitor, or MSI Afterburner to get real-time temperature readings.
- Are higher temperatures always bad for a GPU?
- Occasional spikes are okay during intensive tasks, but consistently high temperatures can cause damage.
- What’s the ideal temperature for my GPU while gaming?
- It’s best to keep it between 60°C to 70°C for optimal performance and longevity.
- Can an overheated GPU cause permanent damage?
- Yes, continuously running a GPU at very high temperatures can shorten its lifespan and cause irreversible damage.
- Does room temperature affect GPU temperature?
- Absolutely! A cooler room can help maintain lower GPU temperatures.
Subscribe to our newsletter
& plug into
the world of PC Hardwares


![[Answered] Can You Turn On a PC Without a Graphics Card?](https://www.hardwarecentric.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/Can-You-Turn-On-a-PC-Without-a-Graphics-Card.webp)
![[SOLVED] New GPU Causing a Black Screen with Cursor? Here’s How to Address It](https://www.hardwarecentric.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/new-graphics-card-black-screen-with-cursor.webp)

