2 MB Intel Smart Cache Technology | Using Between Multiple CPU Cores
The Intel smart cache technology is a method of sharing a level 2 or level 3 cache memory between multiple CPU cores. So, a 2 MB Intel smart cache describes that the processor has either an L2 or an L3 cache of 2 MB that uses smart cache technology to get shared among different cores.

The implementation of smart cache began with the advancement of multi-core processors as dedicated per-core cache was not enough. It reduces the overall rate of cache miss when only some of the cores are working. Besides, it allows a single core to use the entire cache if the rest of the cores are sitting idle.
A Complete Guideline of 2 MB Intel Smart Cache Technology
A 2 MB Intel smart cache means the presence of smart cache technology used for caching in a 2 MB level 2 or level 3 memory.
What Is Smart Cache in Intel?
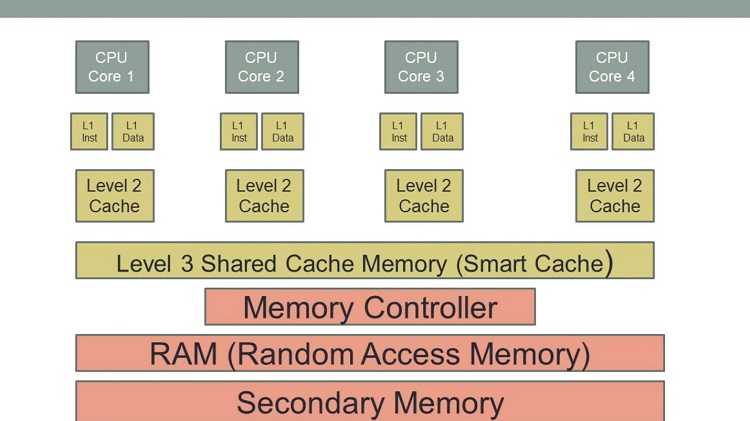
The smart cache is basically Intel’s way of representing shared cache memory. Modern CPUs come with built-in cache memories for faster performance and lower latency. Though RAMs are significantly fast, fetching data from the cache is quicker since it sits right next to the CPU cores.
If you see the memory hierarchy, the cache memory is placed right at the top, followed by RAM and other storage devices like HDDs and SSDs. And because the cache is the fastest and most expensive form of memory, we see such small cache sizes in CPUs.
Generally, most processors feature three levels of cache, L1, L2, and L3. Before, Intel processors had predefined L1 and L2 cache units for each core.
That means core 1 had access to its L1 cache while core 2 could only make use of its own.
So, even when core 2 needed more cache and core 1 barely used its assigned cache, core 2 would have to wait until the next lot of data got fetched.
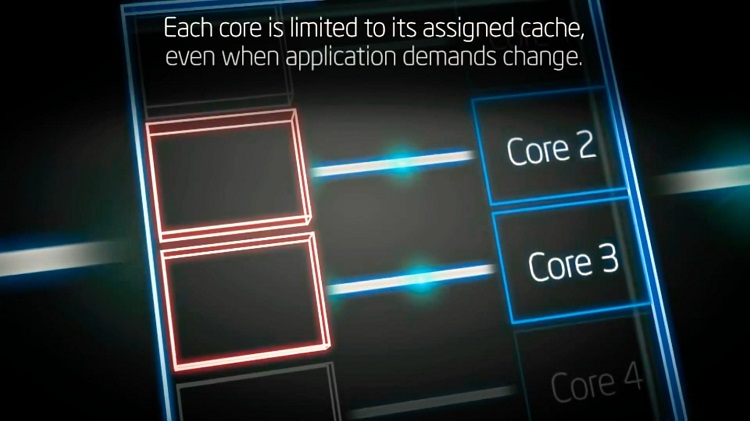
And since the cores had such limited cache resources, there was a noticeable delay in executing large programs. As a solution, Intel implemented the idea of sharing the L2 cache among CPU cores, naming it smart cache.
What Is the Importance of Intel Smart Cache?
Unlike assigned cache memories, the smart cache is adaptive, changing the allocation according to requirements. For example, if a shared cache is 2 MB and core 1 demands 1.5 MB while core 2 can work with less memory, the allocation would follow. As a result, the cores are no longer restricted to their assigned cache memory.
What Are the Drawbacks of Intel Smart Cache?
Although smart cache offers improved processor performance, it also comes with a few drawbacks. For example, sometimes it skips caching highly important data keeping in prior. It can possibly occur performance degradation as users failed to access those data first. Another noticeable drawback is it uses more storage space in order to cache the frequently used data.

Frequently Asked Questions and Answers (FAQs)
Is Smart Cache Better?
Yes, it is. Intel smart cache boosts CPU performance by reducing latency while gaming and performing day-to-day tasks. Moreover, it increases the overall efficiency as the CPU can get more done with the same amount of cache. So, the Intel smart cache technology is here to stay until the next breakthrough.
Is 2 MB Cache Memory Good?
When it comes to cache memory, numbers don’t tell the entire story. With that said, a larger cache size does not necessarily mean better performance and vice versa. Instead, it all boils down to its speed and efficiency in handling data transfer to multiple cores.
Bottom Line
In conclusion, if you come across a 2 MB Intel smart cache and a 2 MB cache without any mention of smart cache, consider the former to be superior. That is because it will make sharing memory among the execution cores faster. Hence, the CPU will perform its best, with minimum latency and cache miss rate.
Subscribe to our newsletter
& plug into
the world of PC Hardwares


![[2 Fixes] 15c20b67-12e7-4bb6-92bb-7aff07997402: DistributedCOM error 10016](https://www.hardwarecentric.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/15c20b67-12e7-4bb6-92bb-7aff07997402.jpg)