LGA 1151 CPU Socket in 1150 Socket of Motherboard | Can It Fit In?
Intel puts numbers like 1150, 1151, and 1155 after LGA (Land Grid Array) to disclose the number of pins in a socket. These pins are there to connect with contact pads located on a processor. And if you put 1151 CPU in 1150 socket, you’re trying to connect 1151 pins with a socket that has only 1150.
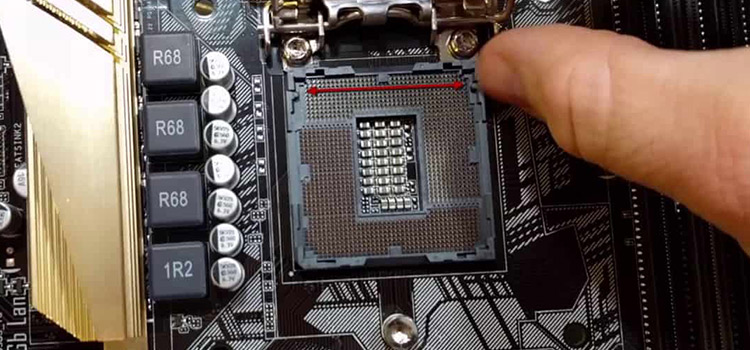
LGA 1151 CPU Socket in 1150 Socket of Motherboard – How Is It?
Though the difference is only one protruding pin, the 1151 CPU is not compatible with an 1150 socket. No matter what DIY technique you apply, you cannot make them work together.
What Does LGA 1150 Mean?
LGA 1150 is the H3 socket used by CPUs based on the Haswell microarchitecture. Besides, it is also used in the Broadwell microarchitecture, a successor of the former. And the LGA 1150 itself is a past iteration of the newer LGA 1151 that came out in 2015.
So, it is clear that CPUs released before 2015 are usually compatible with this motherboard socket. Generally, these processors have outdated RAM support as well as older video outputs. Such an example is the Intel Core i7-4790K, a powerful yet somewhat old chipset.
Are LGA 1150 and LGA 1151 the Same?
They are not the same as Intel designed the LGA 1151 socket to replace the LGA 1150. For those unfamiliar, LGA 1151 is also known as the H4 socket, the later edition of the H3 one. Therefore, the supported processors are the latest ones, with DDR4 RAM and modern video output connections.
Unlike 1150 motherboards, the 1151 ones support recent chipsets like the Skylake, Kaby Lake, and Coffee Lake from Intel. So, they are two separate generations of motherboard sockets that accept different CPUs with different numbers of pins.
Is It Possible to Connet 1151 CPU in the 1150 Socket?
When it comes to connecting CPUs to motherboards, the rule of thumb is to match the numbers written. For example, if a CPU is marked 1150, it will only be compatible with an 1150 motherboard. Likewise, you will need an 1151 socket for an 1151 CPU. Most importantly, they are not interchangeable by any means.
What is the Compatibility of the LGA 1150 CPU Socket?
The LGA 1150 CPU socket, aka H3 socket, is the newer iteration of the LGA 1155. Unlike the older version, 1150 sockets are compatible with several Intel processors starting from as old as dual-core Pentiums to new octa-core i7 processors. However, the support stops after 5th gen Intel processors.
Besides, it is compatible with a handful of Broadwell and Haswell processors as well. For the ports, motherboards with 1150 sockets have support for DVI, VGA, and also HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface). Other than that, they have an integrated memory controller of the RAM type DDR3. Hence, 1151 processors with DDR4 compatibility won’t work.
Can an LGA 1151 CPU Work in an LGA 1150 Motherboard?
To put it simply, an LGA 1151 CPU cannot work in an LGA 1150 motherboard mainly because it has an extra pin. While there are only 1150 pins on the socket of the motherboard, the CPU has 1151. So, there is a lack of collaboration between their architectures, resulting in a misfit.
Yet, if you somehow manage to fit the CPU in an 1150 socket, they won’t be compatible. That is because an LGA 1150 Haswell CPU has a memory controller for DDR3 RAMs, unlike the DDR4 memory controller found in 1151 Skylake and Kaby Lake CPUs.
1. Hurdles with Other Sockets
Also, note that the Coffee Lake and Kaby Lake sockets don’t accept the same CPUs despite being identical physically. Hence, it won’t be quite right to expect distinct sockets to hold the same CPU. And that’s just how Intel makes them, leaving no other option but to match them correctly.
2. Firmware won’t Support
Physical configurations aside, let’s assume we can somehow connect the 1151 CPU to an 1150 motherboard. Even after that, they will not be compatible as the firmware on the motherboard will fail to identify the CPU. Consequently, the computer won’t be able to pass the POST and thereby will not boot.
Summary
Since the 1151 CPU works with newer generation 1151 motherboards only, it is incompatible with the older version. So, putting 1151 CPU in an 1150 socket is not something Intel recommends. Worst of all, there isn’t any third-party converter or intermediary socket that can get the job done either.
Subscribe to our newsletter
& plug into
the world of PC Hardwares